Understanding Interval Problems: The Meeting Room Scheduler
Learn how interval problems work through a relatable meeting room scheduler analogy. Understand the fundamental technique for managing overlapping time slots efficiently.
Learn how interval problems work through a relatable meeting room scheduler analogy. Understand the fundamental technique for managing overlapping time slots efficiently.
Author
Mr. Oz
Date
Read
5 mins
Level 1
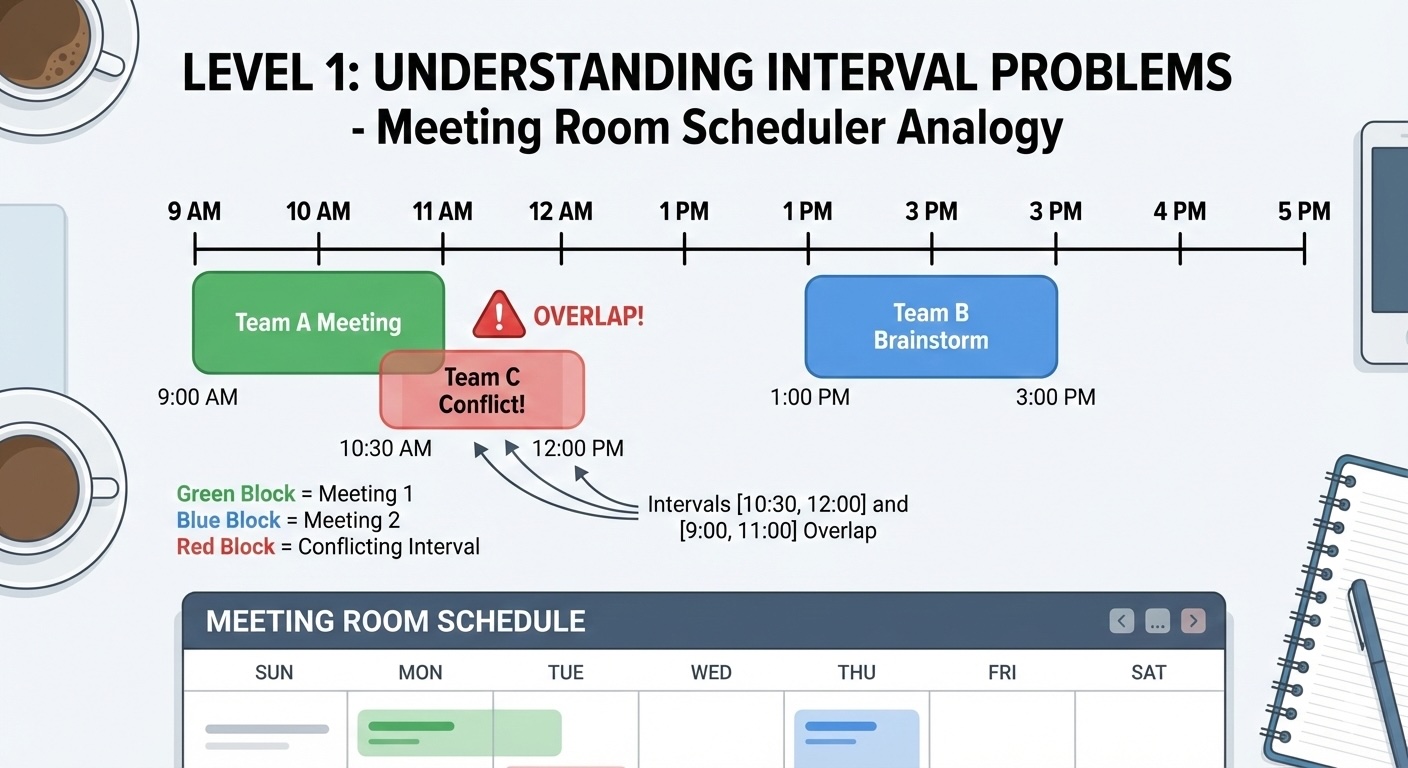
Imagine you're a meeting room coordinator at a busy office. Your job is simple: you receive a list of meeting requests, each with a start time and end time. Your goal is to combine overlapping meetings so the calendar looks clean.
For example, if someone books a meeting from 9 AM to 10 AM and another person books from 9:30 AM to 11 AM, these overlap. Instead of showing two separate meetings, you should combine them into one meeting from 9 AM to 11 AM.
Let's say you have these meeting requests written on sticky notes:
You could try to compare every meeting with every other meeting, but this gets messy quickly. With 10 meetings, you'd make 45 comparisons. With 100 meetings, that's nearly 5,000 comparisons!
This approach works, but it's inefficient and hard to implement correctly.
Here's the key insight that makes interval problems easy:
If you sort all meetings by their start time, overlapping meetings will always be next to each other.
Let's sort our meetings by start time:
Now look at them one by one, and merge if there's overlap:
Final result: [9:00 AM - 10:00 AM], [1:00 PM - 4:00 PM], [5:00 PM - 6:00 PM]
Two intervals [a, b] and [c, d] overlap if:
c ≤ b (the second interval starts before the first one ends)
When they overlap, merge them into:
[a, max(b, d)] (keep the earlier start, take the later end)
Ready to go deeper?
Level 1

Learn interval problems through a relatable meeting room scheduler analogy.
Author
Mr. Oz
Duration
5 mins
Level 2
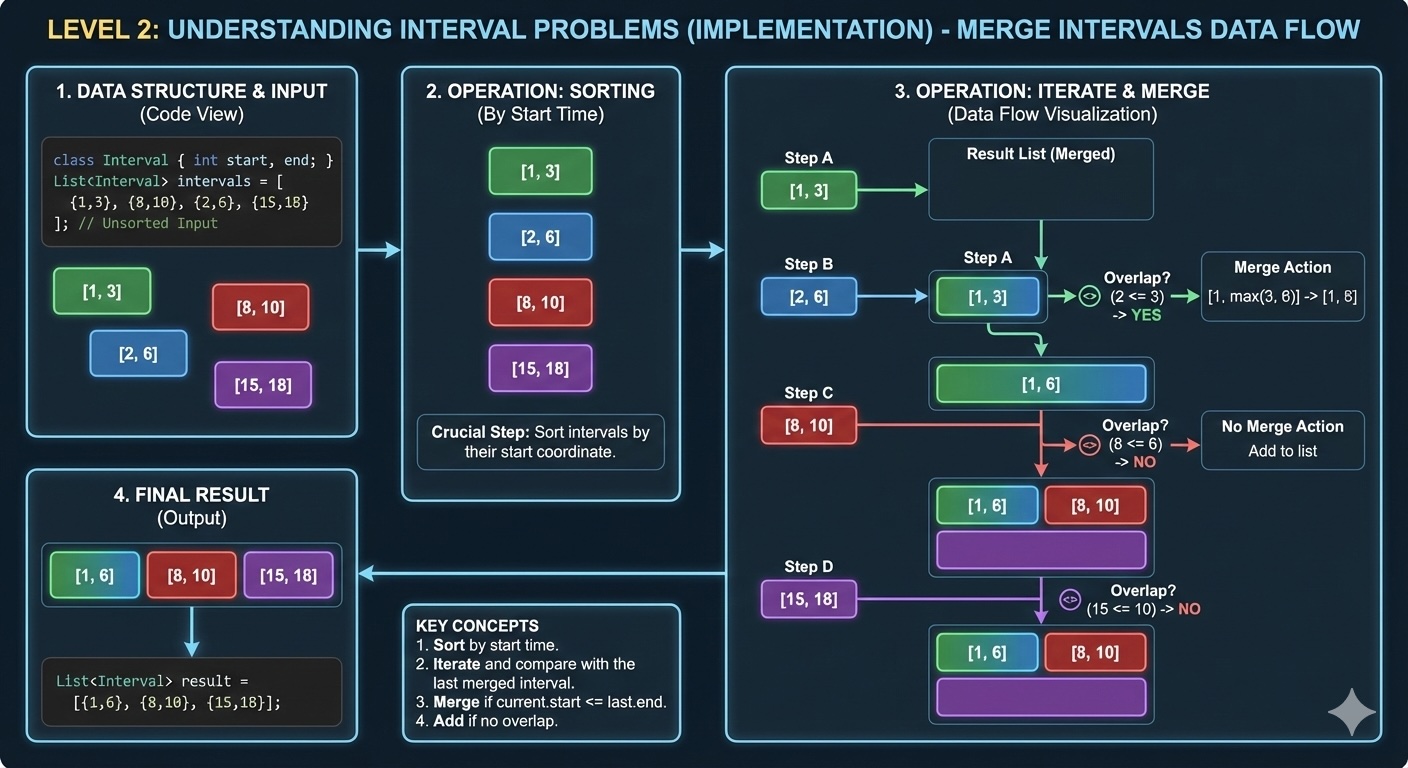
Code implementation in Python, Java, and C++. Learn common patterns and edge cases.
Author
Mr. Oz
Duration
8 mins
Level 3
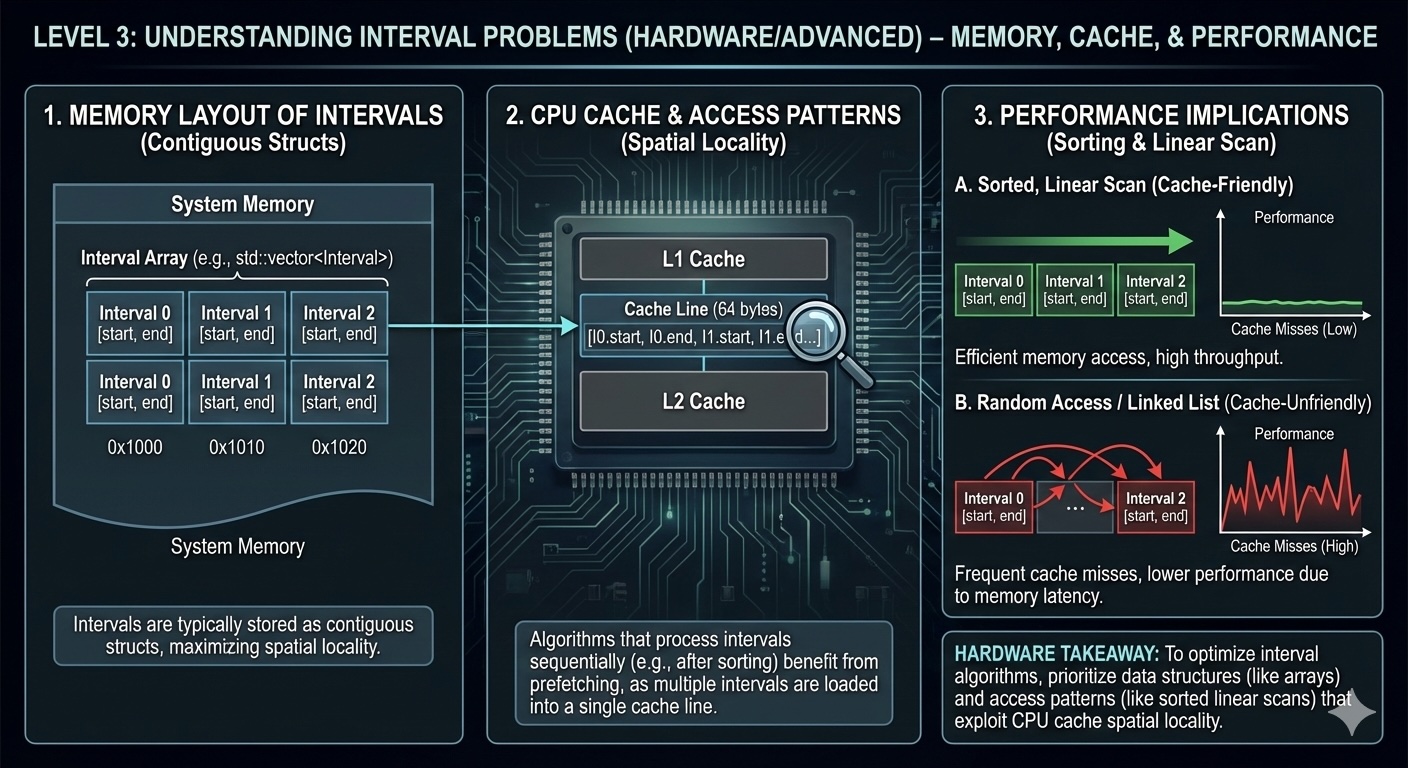
Memory layout, CPU cache considerations, and real-world performance benchmarks.
Author
Mr. Oz
Duration
12 mins