Understanding Dynamic Programming: The Smart To-Do List
Discover how dynamic programming works through an engaging shopping list analogy. Learn why remembering past work makes complex problems trivial.
Discover how dynamic programming works through an engaging shopping list analogy. Learn why remembering past work makes complex problems trivial.
Author
Mr. Oz
Date
Read
5 mins
Level 1
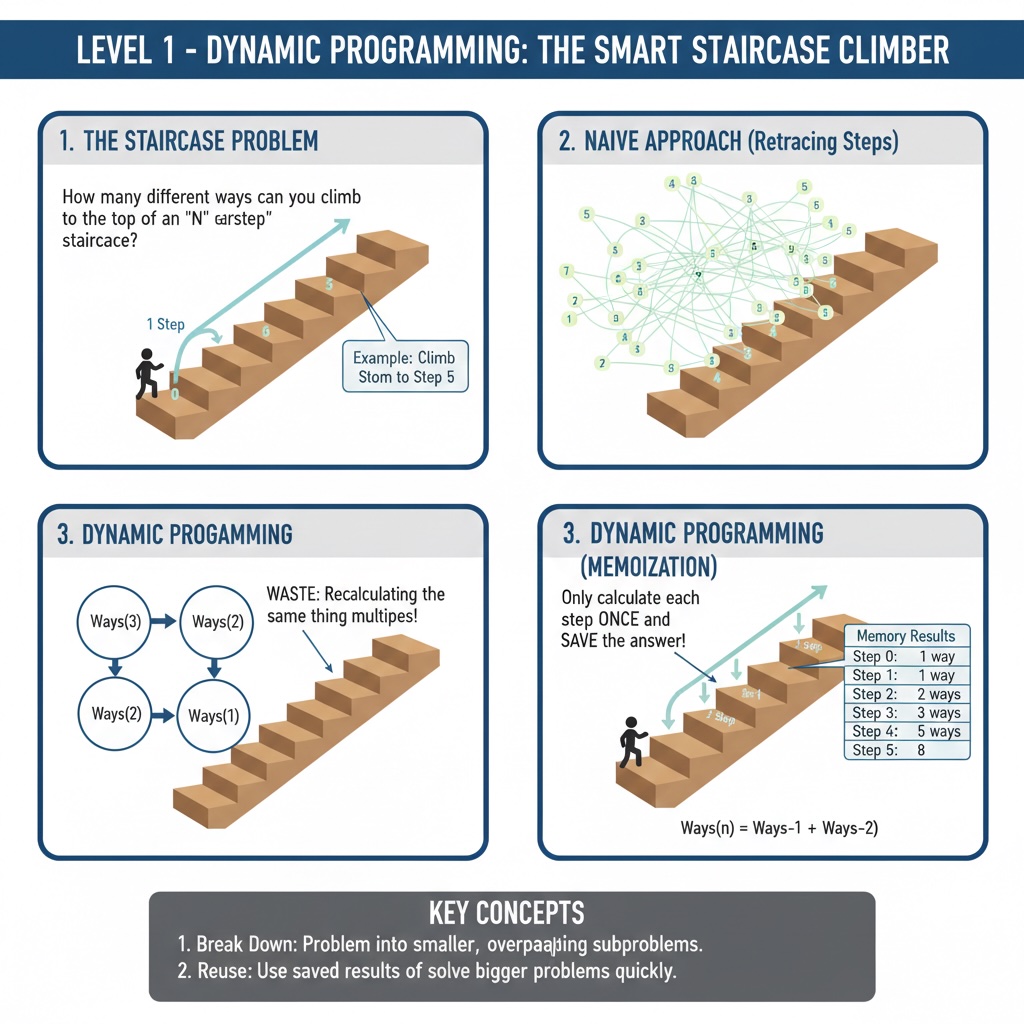
Imagine you're climbing a staircase with 10 steps. You can climb either 1 step or 2 steps at a time. How many different ways can you reach the top?
The hard way: Start from scratch every time. For step 10, you'd have to recalculate all previous steps. This is exhausting!
The smart way: Remember what you calculated before. If you know there are 3 ways to reach step 3 and 5 ways to reach step 4, then step 5 has 3 + 5 = 8 ways!
This smart approach is exactly what dynamic programming does in computer science!
Let's think about this step by step (pun intended!):
Here's the key insight: to reach any step, you must have come from either:
So the total ways to reach the current step equals the sum of ways to reach those two previous steps!
As you calculate each step, something magical appears:
1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89...
This is the famous Fibonacci sequence! Each number is the sum of the two before it.
The staircase problem is Fibonacci in disguise!
Brute Force (without memory):
Dynamic Programming (with memory):
This is just the beginning! In the next level, we'll dive into the code and see exactly how to implement this pattern.
Ready to see the code? Continue to Level 2: Implementation Guide to learn how to implement dynamic programming in Python, Java, and C++!