Understanding Binary Search: Implementation Guide
Learn how to implement binary search correctly with code examples in Python, Java, and C++. Master edge cases, integer overflow prevention, and production-ready patterns.
Learn how to implement binary search correctly with code examples in Python, Java, and C++. Master edge cases, integer overflow prevention, and production-ready patterns.
Author
Mr. Oz
Date
Read
8 mins
Level 2
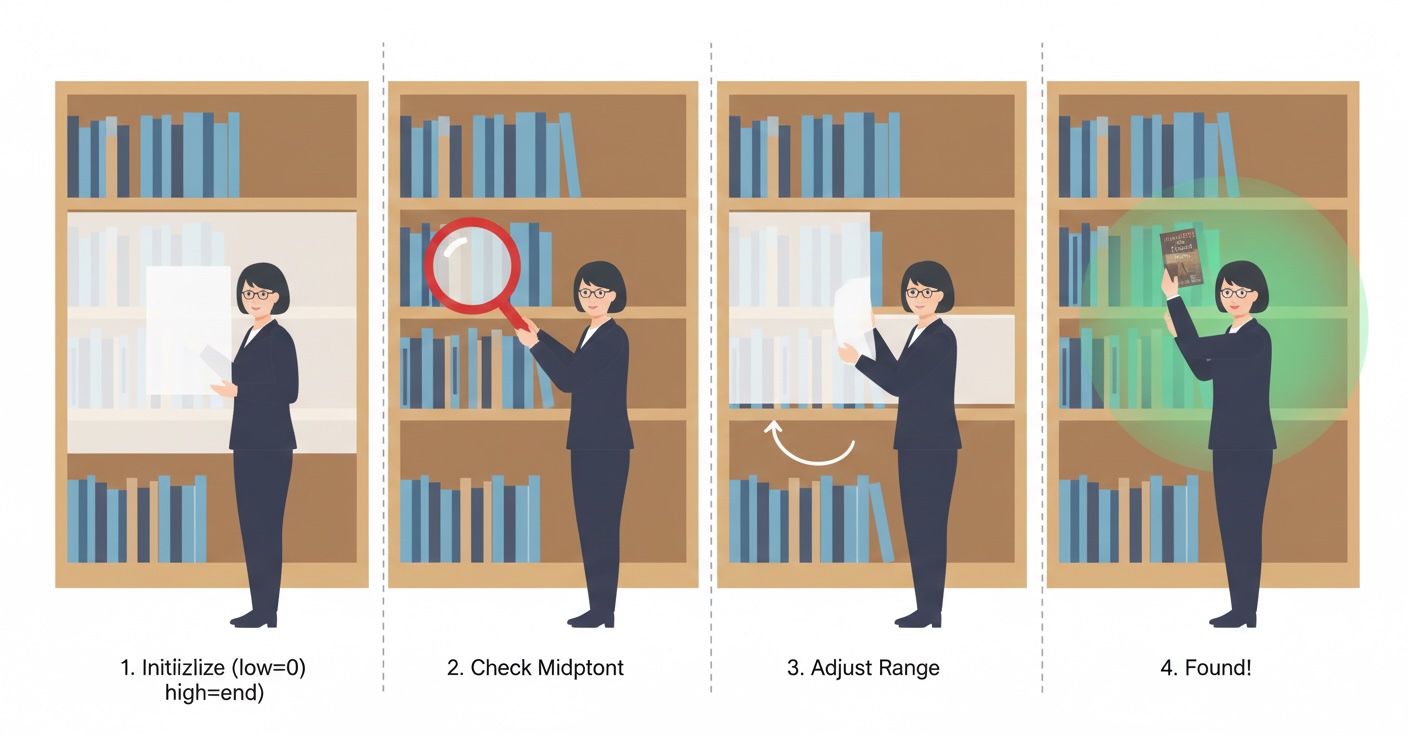
Now that you understand the intuition behind binary search, let's dive into the implementation details. We'll cover code in multiple languages, edge cases, and production-ready patterns.
Here's the basic structure of binary search:
def binary_search(nums, target):
left = 0
right = len(nums) - 1
while left <= right:
mid = left + (right - left) // 2
if nums[mid] == target:
return mid
elif nums[mid] < target:
left = mid + 1
else:
right = mid - 1
return -1 # Not found
Never calculate mid as: mid = (left + right) / 2
Always use: mid = left + (right - left) / 2
Why? Because left + right can overflow when both are large positive integers near the maximum value!
Binary search is O(log n), which means:
Compare this to linear search's O(n) where you might need a million comparisons for a million elements!
left + (right - left) / 2 to prevent overflow
while left <= right (not <)
mid + 1 and mid - 1 (not mid)
Level 1

Learn the fundamentals of binary search through an engaging number guessing game analogy.
Author
Mr. Oz
Duration
5 mins
Level 2

Implementation details, edge cases, integer overflow, and production-ready code examples.
Author
Mr. Oz
Duration
8 mins
Level 3
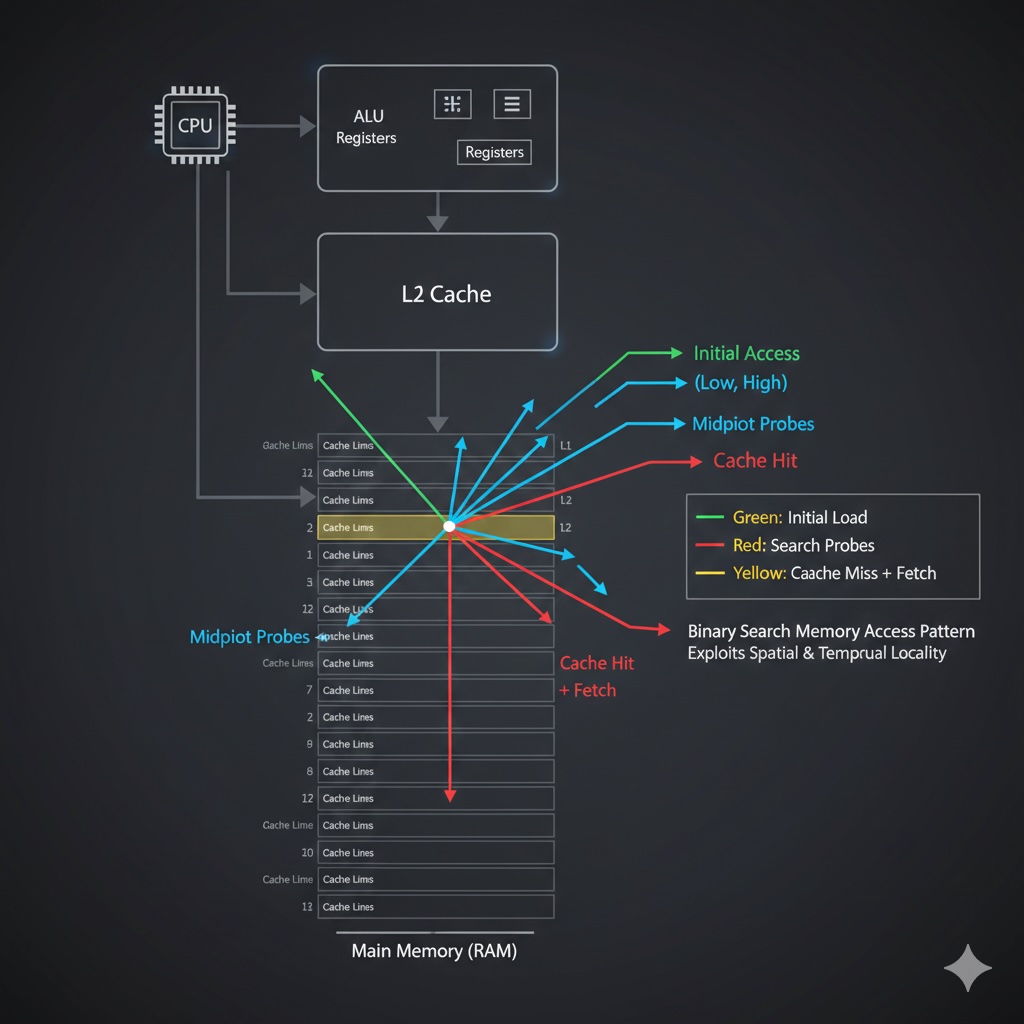
Memory layout, CPU cache performance, branch prediction, and real-world optimization techniques.
Author
Mr. Oz
Duration
12 mins