Understanding Two Pointers — Implementation Guide
Dive into the technical implementation of two pointers technique. Learn common patterns, professional practices, and see code examples in Python, Java, and C++.
Dive into the technical implementation of two pointers technique. Learn common patterns, professional practices, and see code examples in Python, Java, and C++.
Author
Mr. Oz
Date
Read
8 mins
Level 2

One pointer starts at the beginning, another at the end. They move toward each other until they meet.
Common use cases:
Example: Two Sum (Sorted Input)
# Python
def twoSum(numbers, target):
left, right = 0, len(numbers) - 1
while left < right:
current_sum = numbers[left] + numbers[right]
if current_sum == target:
return [left + 1, right + 1]
elif current_sum < target:
left += 1 # Need larger sum
else:
right -= 1 # Need smaller sum
return []Both pointers move in the same direction, but at different speeds or with different timing.
Common use cases:
Example: Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array
# Python
def removeDuplicates(nums):
if not nums:
return 0
# Slow pointer: position to place next unique element
# Fast pointer: scans through array
slow = 0
for fast in range(1, len(nums)):
if nums[fast] != nums[slow]:
slow += 1
nums[slow] = nums[fast]
return slow + 1One pointer leads, exploring ahead. The other follows, processing based on what the leader found.
Common use cases:
Example: Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock
# Python
def maxProfit(prices):
min_price = float('inf')
max_profit = 0
# Single pass with tracked minimum
for price in prices:
profit = price - min_price
max_profit = max(max_profit, profit)
min_price = min(min_price, price)
return max_profitTypical complexities:
Compared to brute force O(n²) approaches, two pointers achieves linear time by eliminating redundant comparisons.
Initialize Pointers Clearly
Always initialize pointers at the start with clear names indicating their purpose.
Pointer Movement Logic
Document WHY each pointer moves. Is it based on comparison? Position? Condition?
Termination Conditions
Clearly define when pointers stop: when they cross? when they meet? when one reaches the end?
Bounds Checking
Always validate pointer positions before accessing array elements to prevent out-of-bounds errors.
❌ Infinite Loops
Forgetting to move one or both pointers in all code paths causes infinite loops.
Fix: Ensure every branch updates pointer positions.
❌ Off-by-One Errors
Using <= instead of < can cause processing the same element twice.
Fix: Trace through small examples to verify boundary conditions.
❌ Wrong Termination
Stopping when left == right vs left > right can miss the last element.
Fix: Be explicit about whether pointers can be equal at termination.
❌ Assuming Sorted Data
Opposite direction pointers require sorted input to work correctly.
Fix: Sort first if needed, or use a different approach.
Ready for advanced optimization techniques?
Level 1

Learn the fundamentals of two pointers through an engaging treasure hunt analogy.
Author
Mr. Oz
Duration
5 mins
Level 2

Implementation details, opposite vs same direction pointers, common patterns, and code examples.
Author
Mr. Oz
Duration
8 mins
Level 3
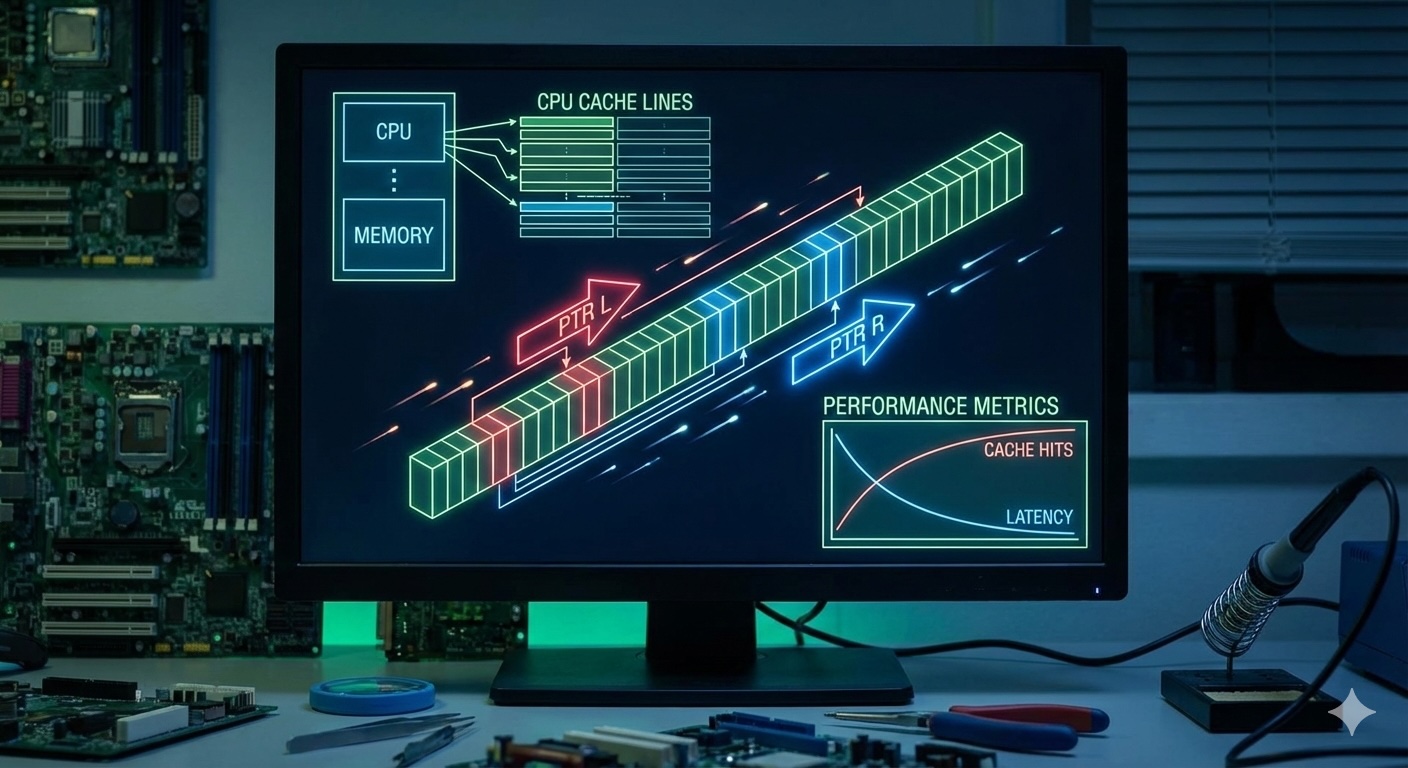
Advanced optimization, cache considerations, and when to use two pointers vs. alternatives.
Author
Mr. Oz
Duration
12 mins